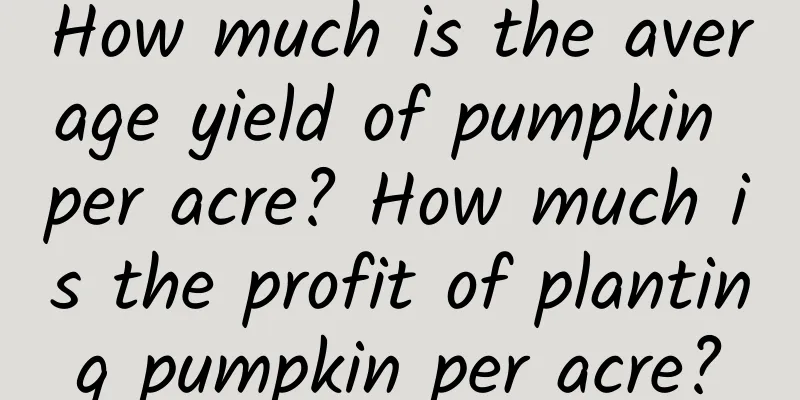Blooming lilies

Morphological characteristics of lilyLily is a perennial bulbous herb with a plant height of 40 to 60 cm, and some are over 1 meter tall. The stem is erect, unbranched, grass green, with red or purple-brown spots at the base of the stem. The leaves are simple, alternate, narrowly linear, without petioles, directly wrapped around the stem, with parallel veins. Some varieties produce purple or green granular bulbils between the leaf axils, which can be propagated into small plants. The flowers are borne at the top of the stem in a raceme, clustered or solitary, with a large corolla and a long, funnel-shaped, trumpet-shaped, six-lobed, and sepal-free. Because the stems are slender and the flowers are large, they often droop or stretch flat when open. The colors vary depending on the variety, mostly yellow, white, pink, orange-red, some have purple or black spots, and there are also flowers with multiple colors, which are extremely beautiful. Some of the petals are flat, while others are curled outwards, hence the beautiful name “Rolling Dandelion”. Some flowers have a strong fragrance, so they are called "musk lilies". The flowers fall and form oblong capsules. Growth habits of liliesLilies prefer cool and humid environments. Places with plenty of sunlight and slightly shady environments are more suitable for lilies. They avoid drought and extreme heat, and have slightly poor cold resistance. The growth and flowering temperature of lily is 16 ~ 24 ℃. Growth almost stops when the temperature is below 5 ℃ or above 30 ℃. The plant grows normally above 10 ℃. When the temperature exceeds 25 ℃, the growth stagnates again. If the night temperature in winter is below 5 ℃ for 5 to 7 days, flower bud differentiation and bud development will be seriously affected, delaying flowering and even causing blind flowers and flower cracks. Lilies prefer fertile, deep soil with a lot of humus, and are most afraid of hard clay; well-drained slightly acidic soil is preferred, with a soil pH of 5.5 to 6.5 . Distribution of liliesLilies are mainly distributed in temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere, including eastern Asia, Europe, and North America. More than a hundred species have been discovered around the world. China is its main place of origin, with more than fifty species native to it, making it the natural distribution center of lily plants. What is the function of lilyOrnamental value: The main application value of lily lies in its ornamental value. Lily is known as the "Fairy in Clouds". Due to its elegant and pure appearance, the Catholic Church regards the lily as a symbol of Mary, while the Vatican regards the lily as a symbol of national independence and economic prosperity and makes it the national flower. The bulb of lily is made up of scales embraced together, which means "a happy marriage for a hundred years" and "everything goes well". Chinese people have regarded it as an indispensable auspicious flower in weddings since ancient times. Lilies have elegant flowers, green and beautiful leaves, and slender stems. They are a valuable new cut flower. Lilies can be used as focal flowers or framework flowers in flower arrangements. It is a special type of flower material. Edible value: The bulbs of lilies are rich in starch, and some varieties can be eaten as vegetables. The Chinese Lanzhou lily, which is famous for its edible value, was first recorded in the annals of Pingliang County, Gansu Province, more than 450 years ago. At present, edible lilies are widely planted in Qilihe, Lanzhou and other areas, and enjoy a high reputation both at home and abroad. Lanzhou lilies are large and sweet, and can be used as snacks or dishes. Lily soup made from Yixing Fritillaria is a great summer refresher. Lily can also be made into dried lily and lily powder, which have a very high price in the international market. Medicinal value: Lily is a commonly used medicinal material in traditional Chinese medicine. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that lily is slightly cold and neutral in nature, and has the effects of clearing heat, moistening the lungs, and calming the nerves. Its flowers and bulbous stems can be used as medicine, and it is a flower that can be used as both medicine and food. |
>>: Margarite flower cultivation methods and precautions
Recommend
How to grow Euphorbia milii in autumn
1. Increase lighting In addition to fertilizing, ...
Spring grass cultivation methods and precautions
1. Maintenance methods 1. Temperature: Spring gra...
How to cultivate water lilies in a water tank without soil
Water lilies have become the choice of more and m...
What is the best month to prune cherry trees?
Cherry tree pruning time There are many times a y...
How to prune and propagate Aquilegia
1. How to trim 1. Pruning time: The pruning time ...
Why do banyan leaves fall off when touched?
1. Long-term water shortage Reason: If the plant ...
What soil to use for agave
1. Several specific requirements (1) Rich in nutr...
What are the cultivation methods and precautions of Cuilan?
Green orchid cultivation method Cuilan, also know...
When does the purple bamboo plum bloom?
1. Flowering period: The flowering period of Purp...
How many sunflowers do you usually give as a gift? What does sunflower mean?
1. How many sunflowers do you usually give? Diffe...
What is the reason for the water content of succulents and how to remedy it
1. Drain water in time The main reason for succul...
What are the benefits of keeping a lucky charm at home?
Hongyun Dangtou creates a natural oxygen bar for ...
Take you to magical South Africa to see succulents, it will be an eye-opener!
Compared with those beautiful flesh in Japan, all...
What fertilizer is good for growing pumpkins?
Pumpkin Fertilizer About 10 days after the pumpki...
Cultivation and propagation methods of Gloxinia flowers
The flowers of Gloxinia have a velvety touch and ...