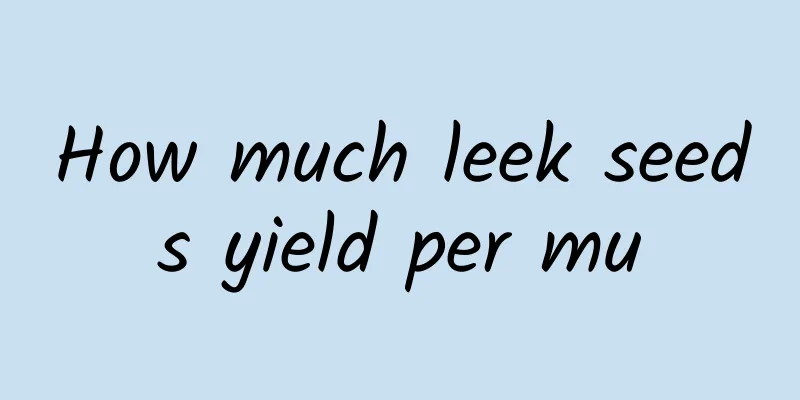A complete monthly calendar for the care of indoor foliage plants

JanuaryCold and dry weather Check the anti-cold measures at any time. If the indoor temperature is not enough, it should be strengthened in time: high-temperature-loving plants can be placed in an incubator made of plastic film or glass to improve the insulation effect. Most plants can receive sufficient sunlight. When there is insufficient light, artificial light can be used to supplement the light. At night, the flower pots should be placed 1 meter away from doors and windows, and can also be covered to keep out the cold. Place dormant plants in a dark place during the winter. Continue to control water and stop fertilizing. Water once every 3-4 days or longer, not ten times. The water temperature should be equal to or slightly higher than the air temperature, and water at noon. For dormant plants in winter, just keep the soil in the pot at a certain humidity. Indoor heating often leads to low air humidity. You can wipe the leaves frequently with a damp cloth to keep them moisturized and clean. FebruaryCold and dry weather During the day, place semi-shade and light-loving plants on the south-facing windowsill to receive sufficient light. At night, place it 1 meter away from the windowsill, or add a cover to keep it warm. Plants that like high temperatures need to be covered with plastic film or placed in a glass incubator during the day. If conditions permit, artificial light can be used to supplement the light to increase the amount of light. For rooms with low room temperature, heating measures should be taken to prevent frost damage. Place shade-tolerant plants in a bright place, and dormant plants in a dark place. Water once every 4 days or more, when the soil is dry, white and hard: do not apply fertilizer or apply a small amount of potassium fertilizer. Wipe the leaves with a damp cloth to remove dust and keep them moisturized. Dead branches and yellow leaves should be cut off in time. MarchCold and dry climate with occasional warm days Maintain light and temperature the same as in February. Even if warm weather occurs occasionally, do not suddenly move the plant outdoors to bask in the sun or remove the insulation facilities, otherwise it will easily cause frostbite. Water and fertilizer control is the same as in February. Cold-tolerant plants begin to be potted up, repotted and repotted. For example, roses and chrysanthemums, etc., they must be planted in warm weather in the second half of the month. AprilThe temperature begins to rise and the light intensity gradually increases, but there is still a cold front. Except for high-temperature-loving and some medium-temperature plants that continue to take anti-freeze measures, the remaining plants can gradually remove the insulation facilities to adapt to the room temperature and provide adequate ventilation, but they still cannot be moved outdoors immediately and can take turns to be exposed to the sun. Maintain humidity, apply small amounts of fertilizer, and increase watering frequency appropriately to create conditions for plant germination, but the soil should not be too wet, and maintain a certain air humidity. In warm weather, water the leaves appropriately at noon. Apply a small amount of complete fertilizer or fertilizer heavy in nitrogen and phosphorus. Most of them can start to repot, and combine repotting with root pruning, posture adjustment, application of base fertilizer, division propagation, etc. MayThe temperature continues to rise, the sun is abundant, the rain begins to increase, and most plants begin to sprout. Some of the heat-loving plants still need insulation management. Most plants can receive sufficient sunlight and proper ventilation. Light-loving and cold-resistant plants can be gradually trained and placed outdoors in rotational light to maintain their good appearance. Except for those that have just been potted, turned over or repotted, the rest can be fertilized. The seedlings and cuttings have begun to grow normally and can also be applied with thin fertilizer and water. Water more frequently, water when the soil is dry, spray the leaves frequently to increase air humidity. Continue to work on potting, repotting and changing pots. As the plants sprout and unfold their leaves, top and pinch the leaves in time. Rubber trees, purple-backed acanthus trees, etc. are heavily pruned and renewed. Tie climbing plants to supports. JuneAs the temperature rises, the sun becomes more abundant, and the rainfall increases, plant growth begins to accelerate. First of all, shade and shelter are provided for shade-tolerant and semi-shade plants to prevent them from being scorched by the sun, and proper ventilation is ensured. The rest of the plants can receive full sunlight to promote lush branches and leaves. Top dressing can be done before watering, and the frequency and amount can be increased appropriately, but be careful to prevent contamination of the stems and leaves. After top dressing, water and spray the leaves in time. Watering is basically once a day, either in the morning or evening, and the number of times you spray water on the leaves should be increased. Repot or repot red mulberry, Schefflera arborvitae, etc. On rainy days, thin out and transplant the seedlings. JulyThe temperature rises, the humidity is high, the sun is strong, and plants grow rapidly. Cold-sensitive plants also enter the growth period Provide shade and sun protection for shade-tolerant and semi-shade plants, and pay attention to indoor ventilation. Provide sufficient water and pay attention to maintaining air humidity in sunny and hot weather. The frequency and amount of topdressing should be increased. Pay attention to preventing diseases and pests this month. Because the hot and humid weather is particularly prone to fungal diseases, spray Bordeaux mixture once every 7-10 days. If any pests or diseases are found, they should be isolated and treated in time. AugustThe climate is hot, with frequent extremely high temperatures. Although the precipitation is large, it is mostly surface runoff. The air humidity is low, which has an adverse effect on plant growth. The main measures include shading, spraying water, ventilation and cooling, and humidification. Different degrees of shading and sun-avoiding measures should be taken for shade-tolerant, semi-shade and light-tolerant plants. In hot and dry weather, some light-loving plants also need a certain degree of shade at noon. Special attention should be paid to cuttings and sowing seedlings. Strengthen ventilation and air permeability measures. Watering must be sufficient and timely. On dry days, watering can be done twice a day, morning and evening. Avoid watering at noon. Place a water basin and increase the number of times you spray water on the leaves and the ground to achieve a cooling and moisturizing effect. Top dressing should be thin fertilizer, mainly nitrogen fertilizer, applied before watering. Control water and fertilizer for summer-dormant plants. When the spores of green cloud grass and ferns are mature, they can be collected and sown for reproduction at any time. Red mulberry, Schefflera arborvitae, etc. can continue to be propagated by cuttings. Actively prevent and control diseases and pests. Same as July. SeptemberThe climate is hot and dry, with extremely high temperatures still occurring. The temperature difference between day and night is large in the second half of the month, which is conducive to plant growth. Light and temperature management are the same as in August. Water and topdressing management are the same as in August. OctoberThe temperature gradually drops, the temperature difference between day and night is large, it is cool in the morning and evening, and most plants have a second growth peak Some semi-shade plants gradually begin to receive direct sunlight. Light-loving plants can get full light throughout the day, but they still need ventilation. The amount of watering remains sufficient and the air humidity is maintained. The amount and frequency of topdressing should be kept the same, and the proportion of potassium fertilizer should be gradually increased and the proportion of nitrogen fertilizer should be reduced. Lucky grass, calla lily, etc. are propagated by division. Proper shaping and pruning. NovemberAs the climate cools, plant growth slows Except for shade-tolerant plants, the rest of the plants gradually receive full sunlight. Plants that are not cold-resistant are gradually moved indoors. For plants whose growth gradually weakens, apply fertilizer once in the first ten days of the month, and then start controlling water and fertilizer. For normally growing plants, the amount of water should not be too much to prevent them from growing too tall, which will lead to a decrease in cold resistance. Fertilizer should mainly be potassium. DecemberThe temperature dropped significantly and the first cold wave began to appear The growth of most plants slows down, and a few plants gradually enter a dormant period. Except for cold-resistant plants, all other plants should be brought indoors. Take measures to block the gaps in doors and windows to prevent the invasion of cold air at any time. Except for shade-tolerant plants, all others can receive full sunlight. For plants that like high temperatures, appropriate insulation measures should be taken depending on the situation, and heating measures should be taken if necessary. The vast majority of plants need to control water and cut off fertilizer, and keep the soil appropriately dry. Keep trimming at all times to maintain good posture. Store pruned branches properly. |
<<: Cultivation methods and precautions of wood fragrance flower
>>: Elderberry cultivation methods and precautions
Recommend
Is it good to keep jasmine at home?
1. Is Feng Shui good? It is very good feng shui t...
Rose rooted and transplanted to a large pot died (how to transfer to soil culture after hydroponic rooting to increase the survival rate)
Why did the rose die after taking root and transp...
Can lilies be exposed to the sun? Can they be exposed to the sun?
Can lilies be exposed to the sun? Lilies can and ...
Does the bean curd flower?
Does the bean curd flower? The evergreen will blo...
The difference between coral tree and bachelor tree
1. Differences in leaves The leaves of the coral ...
How many years does August melon bear fruit?
Introduction to planting wax gourd The wax gourd ...
How to grow colorful trachelospermum
1. Adequate lighting Ichthyophthirius wucai is a ...
What to do if you water your money tree too much
Overwatering the Money Tree Harms of excessive wa...
Kiwi planting methods and precautions
When to plant kiwi fruit Kiwifruit is planted in ...
Cultivation methods and precautions of golden Buddha's hand
Golden Buddha's Hand is an evergreen plant of...
How to grow Clivia to make it bloom as soon as possible (tips to promote Clivia to bloom early)
Clivia is a flowering plant that many flower love...
How to grow garlic at home
1. Prepare the soil When planting garlic at home,...
How to grow coral beads
1. Breeding methods 1. Substrate: When cultivatin...
Disease prevention and control methods of golden lotus
Leaf spot disease of nasturtium Symptoms and patt...
How to breed Belgian rabbits
The Belgian rabbit, also known as the giant gray ...